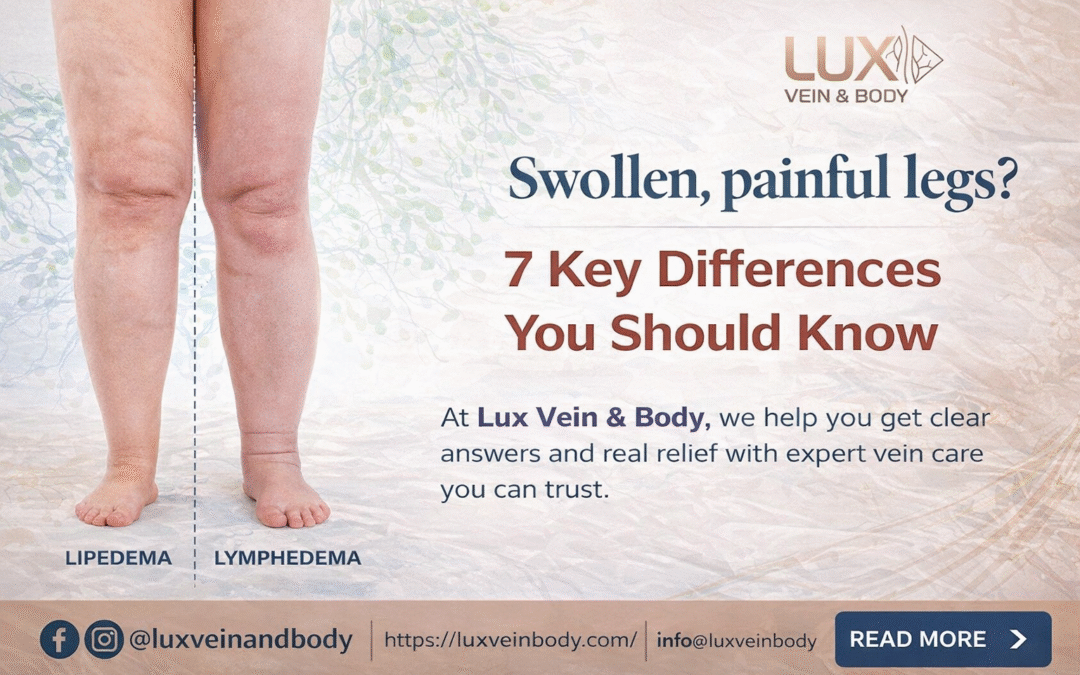
Lipedema vs Lymphedema differences are often misunderstood, even though both conditions cause swelling in the legs or arms. Though they may look similar, they are very different in terms of causes, symptoms, and treatment. This post will help you understand the key differences in simple terms.
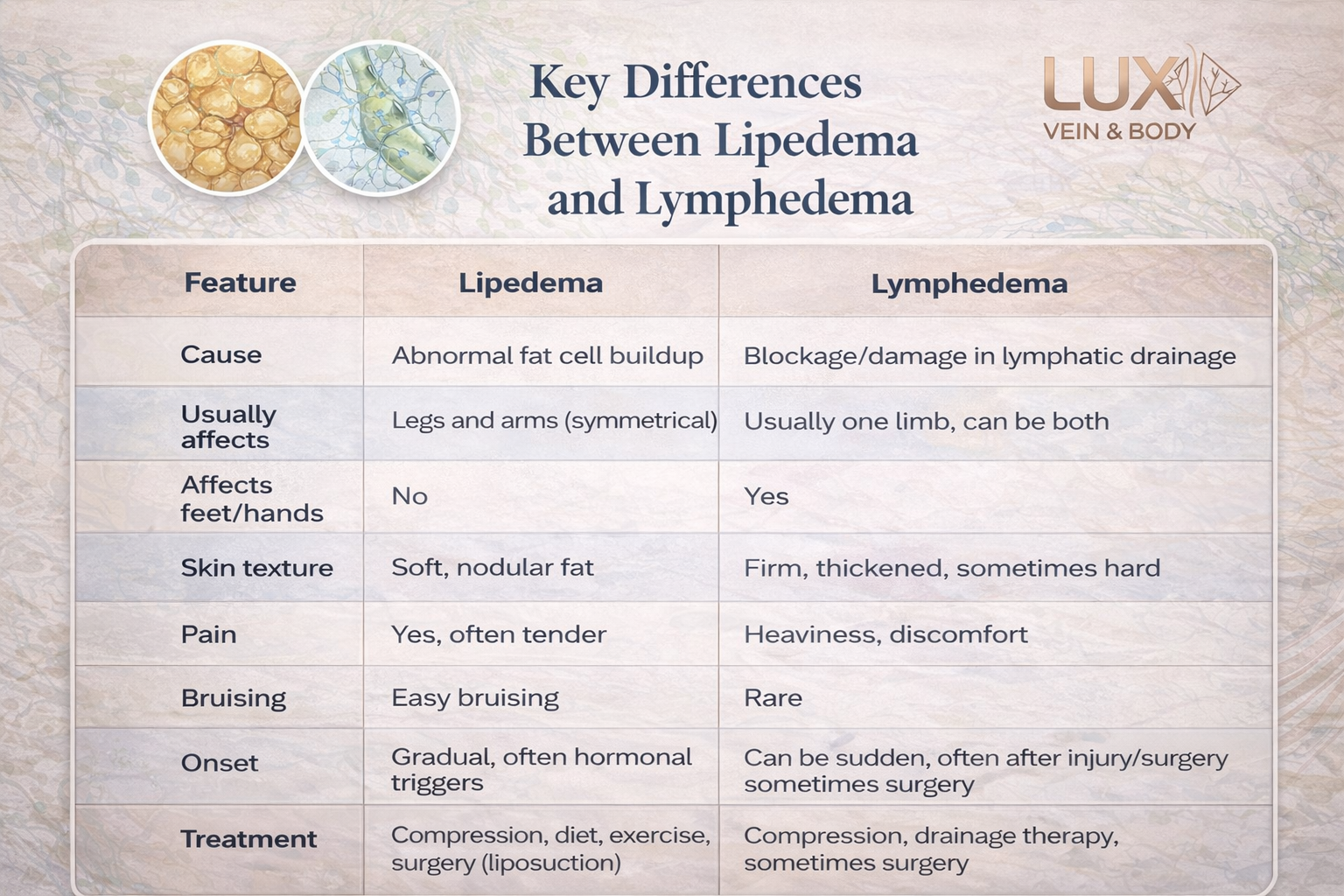
Lipedema is a chronic condition that causes an abnormal buildup of fat cells, usually in the legs and sometimes the arms. It mostly affects women and tends to run in families.
Causes:
- The exact cause is not fully known but is believed to be linked to hormonal changes (often appearing during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause).
- Genetics also play a strong role.
Effects:
- Symmetrical enlargement of legs or arms with fat deposits.
- The skin feels soft but nodular.
- Bruises easily.
- Pain and tenderness in affected areas.
- Swelling worsens over the day but improves with rest.
- Feet and hands are usually not affected, which helps differentiate it from lymphedema.
Lipedema and Venous Insufficiency: What’s the Connection?
People with lipedema often also experience chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), a condition where the veins have difficulty sending blood from the legs back to the heart.
Why Does Venous Insufficiency Occur Lipedema?
- The increased fat deposits and swelling in lipedema can put pressure on veins.
- This pressure interferes with normal blood flow, leading to vein valve dysfunction.
- Hormonal factors and weakened connective tissue may contribute to both conditions.
Effects of Venous Insufficiency in Lipedema:
- Heaviness, aching, and tiredness in the legs.
- Visible varicose veins and spider veins.
- Skin changes, such as dryness or discoloration.
- Increased swelling, especially after standing or sitting for long periods.
Why is This Important?
- Venous insufficiency can worsen lipedema symptoms.
- Treating venous problems alongside lipedema helps reduce discomfort and swelling.
- Compression therapy is especially beneficial because it supports both vein function and lymphatic circulation.

What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is swelling caused by a blockage or damage to the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining excess fluid from tissues.
Causes:
- Can be primary (genetic or developmental issues in the lymphatic system).
- Or secondary, usually caused by injury, surgery, infection, or cancer treatments like lymph node removal or radiation.
Effects:
- Swelling usually starts in one limb but can affect both.
- The swelling is due to a buildup of lymph fluid.
- The skin may feel firm or hardened (fibrosis).
- Can cause heaviness, discomfort, and limited movement.
- Feet and hands are often involved, which is a key difference from lipedema.
- If untreated, it may cause infections like cellulitis.

Treatment Options
Lipedema Treatment
Currently, there is no cure for lipedema, but treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent progression.
- Conservative Management:
- Compression Therapy: Wearing compression garments helps reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming or walking improve circulation and maintain mobility.
- Healthy Diet: While dieting alone doesn’t cure lipedema fat, maintaining a balanced diet can prevent additional weight gain.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): Specialized massage to stimulate lymph flow and reduce swelling.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers and techniques like warm baths may relieve tenderness.
- Surgical Options:
- Liposuction: Specialized techniques (e.g., tumescent or water-assisted) remove excess fat deposits, improving shape and reducing pain.
- Surgery is often considered when conservative methods do not provide relief.
The focus is on reducing swelling and preventing complications.
- Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT):
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage: Specialized massage to move excess lymph fluid.
- Compression Bandaging/Garments: Custom-fitted to maintain reduced limb size.
- Exercise: Light exercises to encourage lymph flow.
- Skin Care: Prevent infections by keeping skin clean and moisturized.
- Other Treatment Approaches:
- Pneumatic Compression Devices: Pumps that apply intermittent pressure to limbs.
- Medications: Antibiotics if infections occur.
- Surgery: In selected cases, procedures like lymphatic bypass or lymph node transfer may be options.

Why is Knowing the Difference Important?
Misdiagnosing lipedema as simple obesity or lymphedema can delay proper treatment. Each condition requires a different management approach to improve quality of life:
- Lipedema treatments focus on reducing fat deposits and pain.
- Lymphedema treatments aim to improve lymph drainage and reduce swelling.
Treatment varies greatly once lipedema vs lymphedema differences are confirmed.

Conclusion
While lipedema vs lymphedema differences both involve swelling, they are caused by different issues and have distinct signs. Understanding lipedema vs lymphedema differences helps patients avoid misdiagnosis.
If you or a loved one experiences persistent swelling, pain, or abnormal fat distribution, consult a healthcare professional who can accurately diagnose and guide treatment.